The Science of Climate Change: Understanding the Global Crisis and How We Can Help

Introduction:
At Genesis Global School, the Top 10 Boarding Schools in Noida where climate change has emerged as one of the most pressing challenges of the 21st century. The impacts of global warming and the alteration of climate patterns are becoming more evident with each passing year, affecting ecosystems, economies, and communities worldwide. To understand this complex issue and explore potential solutions, it is essential to delve into the science behind climate change, examine its far-reaching effects, and consider the role individuals, especially students, can play in mitigating its impact.
In this article, we will break down the science of climate change, its causes and consequences, and explore actionable steps that we can take to help combat the global climate crisis. By doing so, we aim to inspire the next generation to take up the mantle of climate activism and environmental stewardship.
What Is Climate Change?
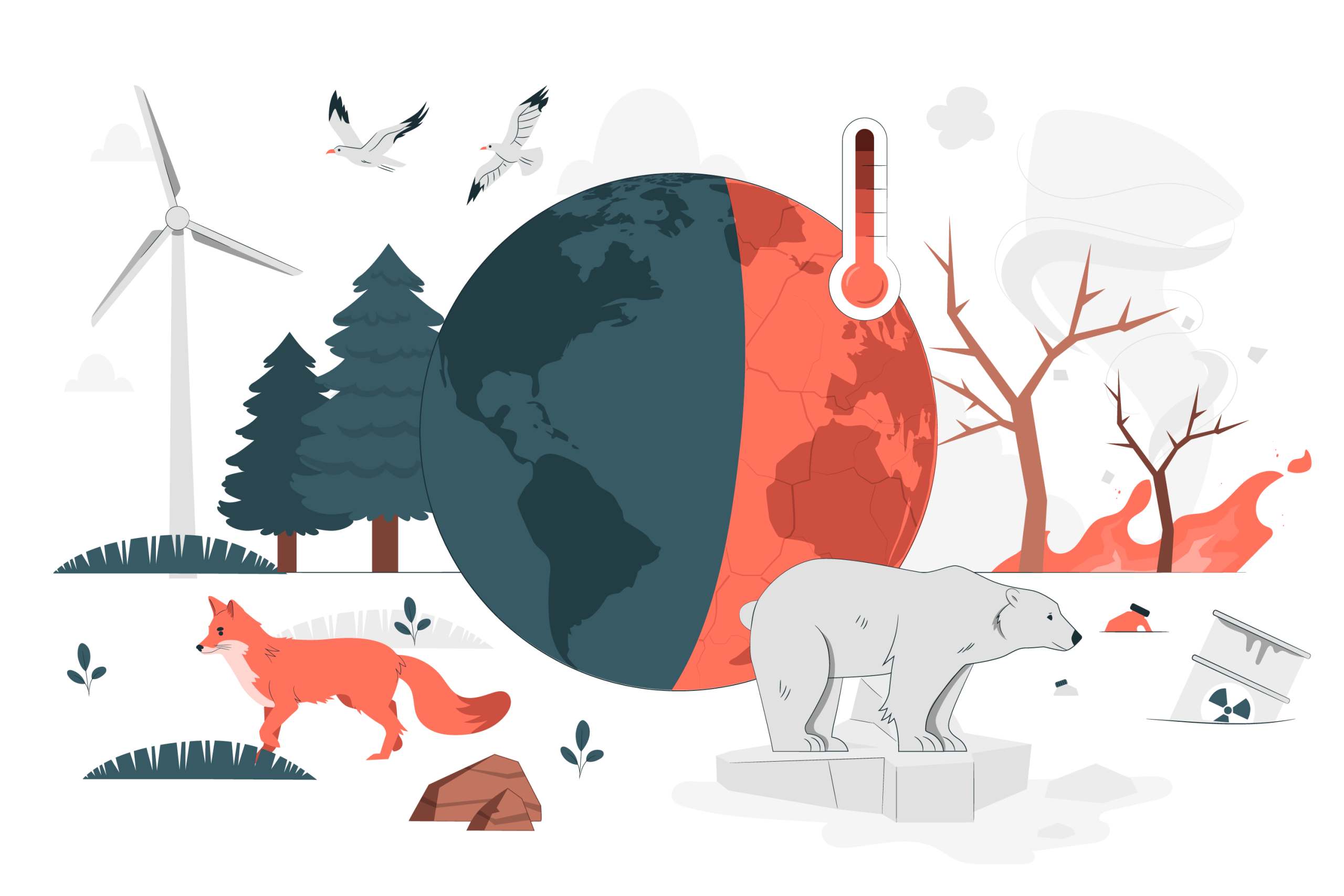
Climate change refers to long-term alterations in the average weather patterns across the globe, which have been observed over an extended period. While Earth’s climate has naturally fluctuated due to various factors, human activities—particularly since the Industrial Revolution—have dramatically accelerated changes in the planet’s climate system. The most significant change observed is the rise in global temperatures, commonly referred to as global warming.
The Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming
At the heart of climate change is the “greenhouse effect.” This natural process helps regulate Earth’s temperature by trapping some of the Sun’s heat in the atmosphere. Greenhouse gases (GHGs), such as carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O), absorb infrared radiation and prevent it from escaping into space. Without the greenhouse effect, Earth would be too cold to support life.
However, human activities—primarily the burning of fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas) for energy, deforestation, and industrial processes—have increased the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, leading to enhanced global warming. Since the late 19th century, the global average temperature has risen by approximately 1.1 degrees Celsius (2 degrees Fahrenheit), with more significant warming expected in the future.
The Causes of Climate Change
Understanding the causes of climate change is crucial to addressing the problem effectively. While natural factors like volcanic eruptions and solar radiation can influence the climate, the primary driver of recent climate change is human activity. The following are the major contributors to the global climate crisis:
- Burning Fossil Fuels
Fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas are the backbone of modern industrialized society. They power our homes, vehicles, and industries. However, the combustion of these fuels releases large quantities of CO2 and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. The burning of fossil fuels accounts for nearly 75% of all human-generated CO2 emissions.
- Deforestation
Forests play a vital role in regulating the Earth’s climate by absorbing CO2 through photosynthesis. However, large-scale deforestation—primarily for agriculture, logging, and urbanization—has significantly reduced the planet’s forest cover. When trees are cut down, not only is their ability to absorb CO2 lost but the carbon stored in the trees is released back into the atmosphere.
- Industrial Processes
Various industrial activities, including cement production, steel manufacturing, and chemical production, generate significant amounts of greenhouse gases. These processes emit CO2, methane, and other pollutants, contributing to climate change. Industrial emissions are a major source of atmospheric GHGs, particularly in rapidly developing economies.
- Agriculture
Agricultural practices, including livestock farming and rice cultivation, release large amounts of methane, a potent greenhouse gas. Additionally, the use of synthetic fertilizers in agriculture results in nitrous oxide emissions. Intensive farming practices also lead to deforestation, land degradation, and increased water usage, all of which exacerbate the climate crisis.
- Waste Management
Improper waste disposal, particularly in landfills, contributes to methane emissions as organic waste decomposes. Moreover, the production and disposal of plastics and other non-biodegradable materials release GHGs and pollutants that contribute to climate change.
The Impacts of Climate Change
Climate change affects every region of the world and has far-reaching consequences for the environment, human health, and economic systems. The following are some of the most significant impacts:
- Rising Temperatures
Global temperatures are increasing, with 2020 tying with 2016 as the hottest year on record. Higher temperatures can cause more frequent heatwaves, which can lead to increased mortality rates, particularly among vulnerable populations such as the elderly and those with preexisting health conditions.
- Melting Ice and Rising Sea Levels
The warming of the Earth has caused polar ice caps and glaciers to melt, leading to rising sea levels. As sea levels rise, coastal areas are increasingly at risk of flooding, which can displace millions of people, damage infrastructure, and destroy ecosystems. Low-lying islands and coastal cities face existential threats due to sea-level rise.
- Extreme Weather Events
Climate change is linked to an increase in the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, floods, droughts, and wildfires. These events cause significant damage to property, infrastructure, and agriculture, leading to economic losses and humanitarian crises.
- Threats to Biodiversity
Rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and habitat loss are pushing many species to the brink of extinction. Coral reefs, for example, are particularly vulnerable to warming oceans, with many reefs experiencing bleaching events that threaten marine ecosystems. Deforestation and climate change also endanger terrestrial species, leading to a loss of biodiversity.
- Impact on Agriculture
Climate change is affecting food security by altering growing seasons, reducing crop yields, and increasing the frequency of extreme weather events such as droughts and floods. Changes in temperature and precipitation can also affect water availability for irrigation, leading to agricultural challenges in many parts of the world.
- Human Health Risks
Climate change poses significant health risks, including increased respiratory diseases due to air pollution, the spread of infectious diseases due to changing ecosystems, and heat-related illnesses during heat waves. The displacement of communities due to rising sea levels and extreme weather events can also lead to mental health issues and increased poverty.
How We Can Help Combat Climate Change
While climate change is a global crisis, individuals, communities, and governments all have a role to play in mitigating its effects. From reducing our carbon footprint to advocating for policy changes, there are many ways we can help combat climate change. Here are some actionable steps that students, educators, and communities can take:
- Reduce Energy Consumption
One of the most effective ways to combat climate change is by reducing energy consumption. Simple actions such as turning off lights when not in use, using energy-efficient appliances, and reducing water heating can significantly lower household energy usage. Additionally, encouraging the use of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, can help reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
- Promote Sustainable Transportation
Transportation is a significant source of greenhouse gas emissions, particularly in urban areas. By using public transportation, walking, cycling, or carpooling, individuals can reduce their carbon footprint. Electric vehicles (EVs) are also becoming more accessible and provide a cleaner alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars.
- Support Reforestation and Conservation
Forests are critical to absorbing CO2 and maintaining biodiversity. Participating in tree-planting initiatives, supporting reforestation projects, and advocating for the protection of natural habitats can contribute to restoring ecosystems and reducing carbon emissions. Schools can also incorporate environmental conservation projects into their curriculum to educate students about the importance of biodiversity.
- Advocate for Climate-Friendly Policies
Governments and corporations have a significant influence on climate change through the policies they implement. By advocating for climate-friendly policies—such as carbon pricing, renewable energy incentives, and stricter emissions regulations—students and citizens can push for systemic changes that promote sustainability.
- Reduce, Reuse, Recycle
Waste management plays a crucial role in mitigating climate change. Reducing waste production by avoiding single-use plastics, reusing materials, and recycling can significantly lower the amount of waste that ends up in landfills, where it contributes to methane emissions. Schools and communities can encourage recycling programs and promote sustainable consumption habits.
- Educate and Raise Awareness
Raising awareness about climate change is essential for inspiring action. Schools, educators, and students can lead the charge by organizing workshops, seminars, and campaigns that educate others about the causes and effects of climate change. Social media can also be used as a platform to spread awareness and mobilize collective action.
- Adopt Sustainable Eating Habits
The food industry is a significant contributor to climate change, with livestock farming generating large amounts of methane emissions. By reducing meat consumption, supporting plant-based diets, and choosing locally sourced, organic foods, individuals can reduce the environmental impact of their food choices.
- Support Green Innovations
Innovation is critical in the fight against climate change. Supporting companies and startups that are developing green technologies—such as renewable energy systems, sustainable agriculture practices, and eco-friendly products—can help drive the transition to a low-carbon economy. Schools can foster innovation by encouraging students to participate in environmental science projects and sustainability challenges.
The Role of Schools in Combating Climate Change
Schools play a pivotal role in educating the next generation of climate leaders. By incorporating environmental education into the curriculum, schools can equip students with the knowledge and skills needed to tackle climate change. Hands-on projects, such as building renewable energy models, conducting environmental impact assessments, or participating in community clean-up efforts, can give students practical experience in addressing environmental challenges.
Additionally, schools can adopt sustainable practices in their operations, such as reducing energy and water usage, implementing recycling programs, and promoting sustainable transportation options for students and staff. By leading by example, schools can inspire students to take action in their own lives.
Conclusion
At Genesis Global School, the good boarding schools in delhi where climate change is a complex and multifaceted global crisis, but it is not insurmountable. Through a combination of scientific understanding, policy change, and individual action, we can mitigate the worst effects of climate change and build a more sustainable future. The science of climate change provides us with the tools to understand the causes and impacts of this crisis, while actionable steps—such as reducing energy consumption, supporting renewable energy, and advocating for policy changes—offer pathways to positive change.
For students, the fight against climate change presents an opportunity to be part of the solution. By engaging in climate activism, pursuing environmental education, and taking meaningful steps to reduce their carbon footprint, young people can lead the way in creating a greener, more sustainable world. The future depends on the actions we take today, and the next generation has the power to shape that future for the better.
Popular Posts
Recent Posts
Archive
- January 2025
- December 2024
- November 2024
- October 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- May 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
- February 2024
Newsletter
 A1 and A12, SECTOR-132,EXPRESSWAY, NOIDA (201304)
A1 and A12, SECTOR-132,EXPRESSWAY, NOIDA (201304)
 +91-9711000498 / 560 / 625 / 626
+91-9711000498 / 560 / 625 / 626
 info@genesisgs.edu.in
info@genesisgs.edu.in
- Contact Us
- Address
- Mobile Number
- +91-9711000498 / 560 / 625 / 626
- info@genesisgs.edu.in
© Copyright 2018, all rights reserved with Genesis Global School